How to use a VPN on your RDP without disconnecting
How to use a VPN on your RDP without disconnecting
Many users face the same frustrating issue. You install a VPN on your Windows server, enable it, and your RDP connection drops instantly. Nothing is wrong with the server. The problem is simple: most VPN clients reroute all traffic through their tunnel. When this happens, Windows treats the RDP session as just another outbound stream and pushes it into the VPN, which causes an immediate disconnect.
This guide explains why this happens and how to use a VPN on RDP without losing access. You’ll learn which settings matter, how to keep your remote desktop session stable, and which VPN clients work out of the box. Some require extra configuration, but all can run smoothly if you set them up correctly.
VPN Clients That Work Without Any Changes
Some VPN services handle routing gently. They don’t replace the server’s default gateway and therefore avoid the common RDP disconnect issue when using a VPN.
● OpenVPN
● TunnelBear
● Proton VPN
OpenVPN leaves most of the system’s routing table untouched. RDP traffic continues using the original network interface, which keeps the session stable. Even with heavy encryption profiles, OpenVPN rarely forces full-tunnel mode unless you configure it manually.
TunnelBear uses a lightweight driver that doesn’t interfere with local traffic. It creates the VPN tunnel but allows RDP to stay on the standard route. The result is simple: the remote desktop stays alive before, during, and after the connection. No routing rules needed.
Proton VPN maintains RDP stability thanks to balanced routing and a moderate kill-switch. As long as strict modes aren’t enabled, Proton VPN allows RDP and VPN traffic to coexist without conflict. It's a good choice for users who need privacy without losing remote access.
VPN Clients That Require Extra Configuration
Some VPN apps apply strict full-tunnel routing by default. This often leads to the familiar complaint: “VPN breaks my RDP connection.” Fortunately, a few tweaks solve the problem.
● ExpressVPN
● Mullvad
● NordVPN
● WireGuard
ExpressVPN is powerful but uses Network Lock, a kill-switch that immediately breaks RDP. Disable Network Lock and allow local network traffic. After this, ExpressVPN stops tunneling RDP packets, and your session remains alive even with the VPN active.
Mullvad has strict routing policies. To avoid disconnects, enable Local Network Sharing, set custom DNS (1.1.1.1 / 1.0.0.1), and activate Split Tunneling. Add mstsc.exe or any RDP-related process to the exclusion list. Once done, Mullvad and RDP work together without conflict.
NordVPN frequently triggers RDP drops because of its kill-switch. Open the app, enable “Allow remote access while using VPN”, or disable the kill-switch entirely. After adjusting these settings, NordVPN stops intercepting remote desktop traffic and becomes fully compatible with Windows servers.
WireGuard follows your configuration file exactly. If it contains rules like “block untunneled traffic,” RDP will disconnect immediately. Adjust the AllowedIPs field or disable kill-switch behavior. Once fixed, WireGuard can run VPN on RDP without disconnecting or interrupting your session.
ExpressVPN
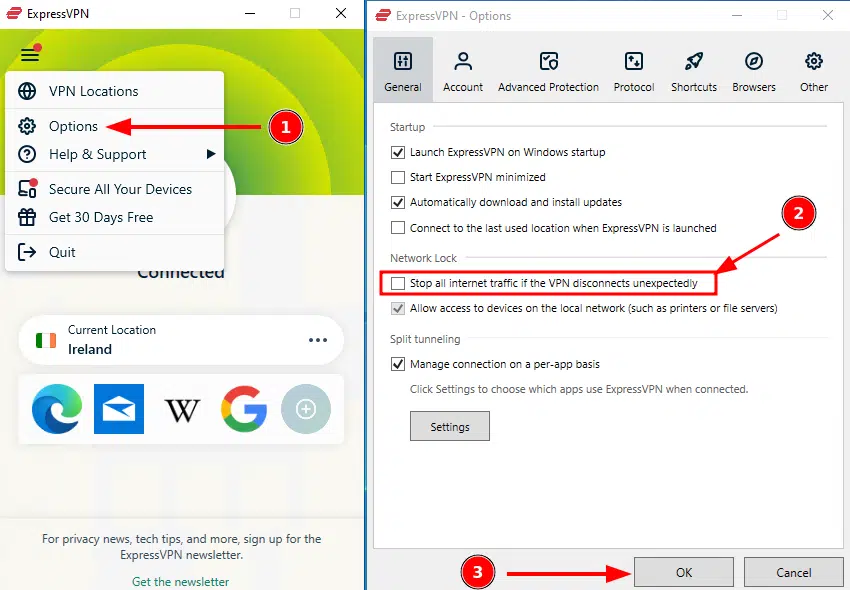
Press the hamburger icon in the top-left of your Express VPN client and choose "Options". Then, untick "Stop all internet traffic if the VPN disconnects unexpectedly" and press "OK".
Mullvad
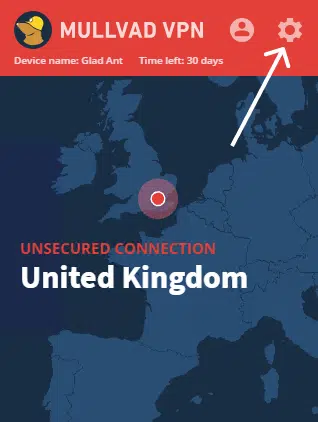
Step 1: Press the settings cog in the top right corner of your Mullvad client.
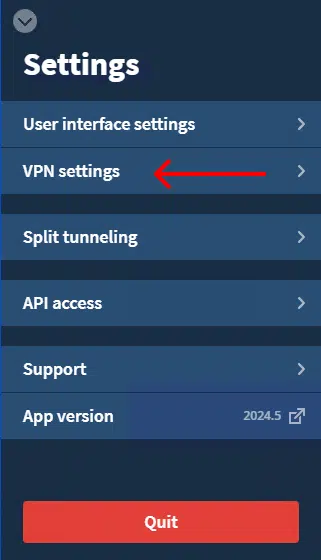
Step 2: Open the "VPN settings" window.
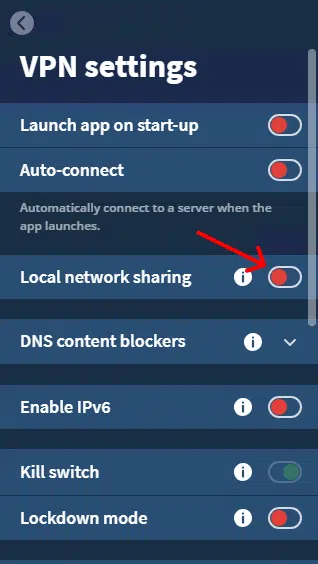
Step 3: Toggle on the "Local network sharing" option.
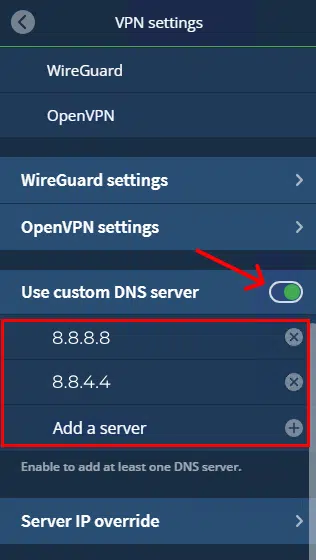
Step 4: Scroll until you see the "Use custom DNS server" option and toggle that on. Under the custom DNS heading, press "Add a server". Add the IP addresses "1.1.1.1" and "1.0.0.1" (or another private DNS provider).
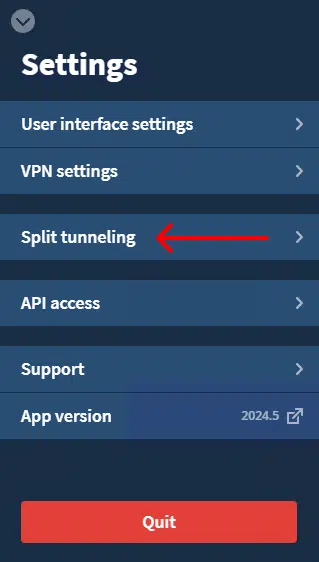
Step 5: Go back to the main settings and open the "Split tunneling" options.
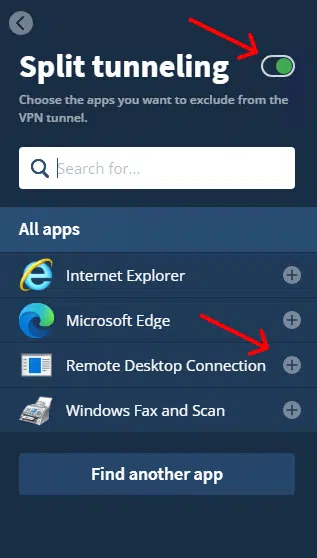
Step 6: Toggle on Split tunneling next to its heading and press the "+" icon next to "Remote Desktop Connection" in the list below.
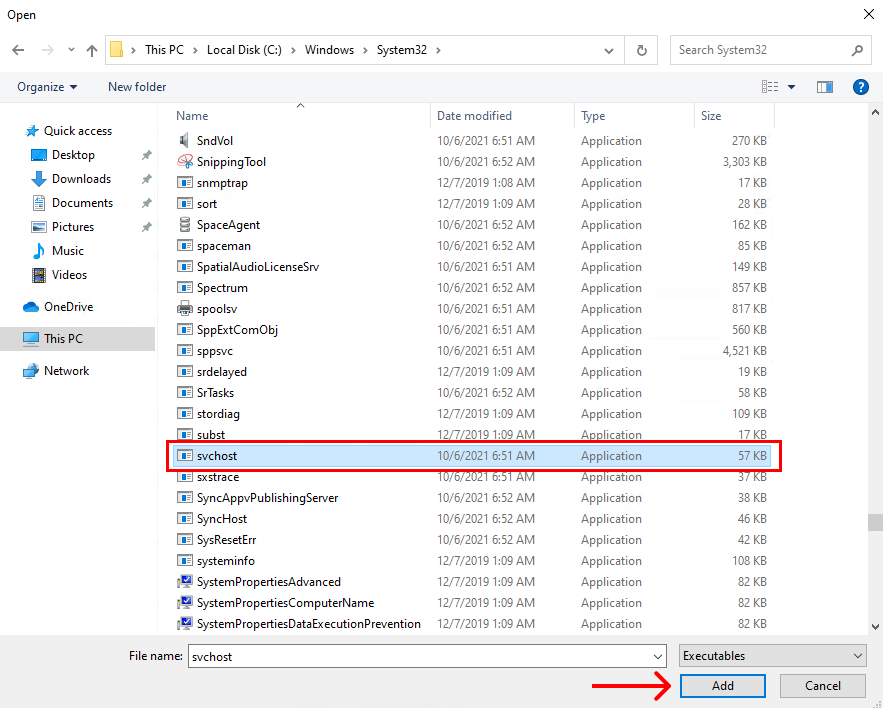
Step 7: While still in the split tunnelling menu, press "Find another app".

Step 8: Navigate to "C:\Windows\System32\", find "svchost.exe", and press "Add".
NordVPN
Step 1: Press the settings cog in the bottom left corner of your VPN client and click "Connection" in the main pane.
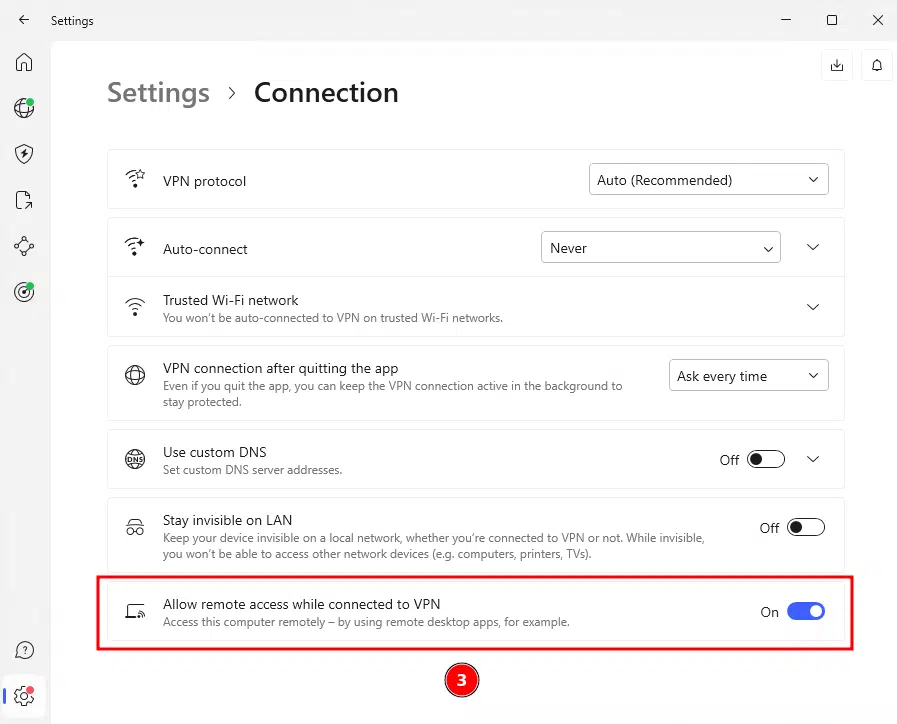
Step 2: Toggle on the "Allow remote access while connected to VPN" option.
WireGuard
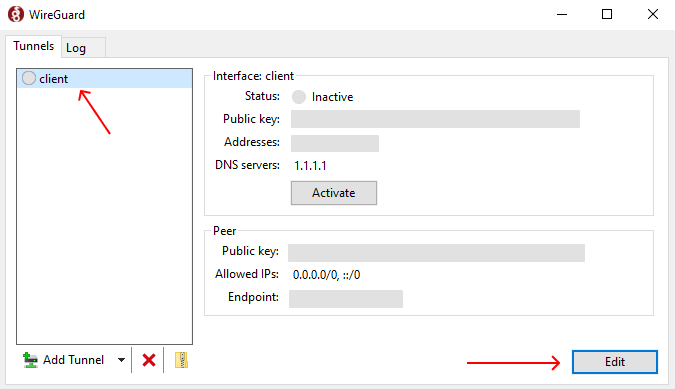
Step 1: Click on the tunnel you use for your VPS server in your WireGuard client and press "Edit" in the bottom right corner.
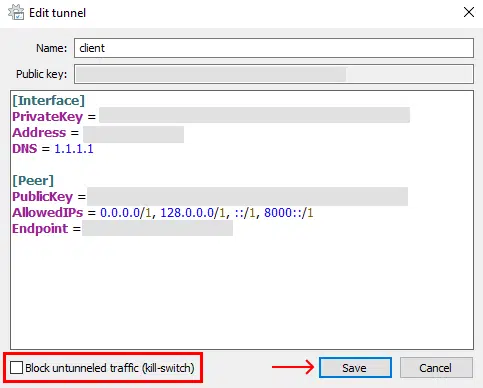
Step 2: Untick "Block untunneled traffic (kill-switch)" in the bottom left corner and press "Save".
Conclusion
A VPN should not break your workflow. The disconnect issue has nothing to do with server stability or your hosting provider — it’s purely a routing problem. After a few small adjustments (or choosing a VPN that doesn’t rewrite the gateway), your RDP session becomes stable again.
With the right configuration, you can encrypt traffic, protect your privacy, and keep your RDP connection alive while using a VPN. Set it up once, and everything runs smoothly without the usual “VPN connected → RDP disconnected” frustration.
FAQ
You ask, and we answer! Here are the most frequently asked questions!
-
Why does my RDP session disconnect when I enable a VPN?
- Most VPN apps replace the server’s default gateway and send all traffic into the tunnel. When this happens, RDP packets no longer reach your client, so the session drops. Disabling the kill switch or enabling split tunneling usually fixes it.
-
Can I use a VPN on RDP without losing access?
- Yes. Many users run a VPN on Windows servers without disconnecting RDP. You only need minor routing changes — allow local network access, exclude RDP from the tunnel, or disable full-tunnel mode. After that, the connection stays stable.
-
Which VPN works best with RDP?
- OpenVPN, TunnelBear, and Proton VPN work without changes. ExpressVPN, NordVPN, Mullvad, and WireGuard need small adjustments, like disabling the kill switch or enabling split tunneling, to prevent RDP drops.
-
Is split tunneling safe on a Windows server?
- Yes. When configured properly, it keeps RDP outside the VPN tunnel while your sensitive traffic stays encrypted. Many administrators prefer this setup because it maintains privacy and preserves remote access.
